1. Nature Reviews Materials Review: DNA Nanotechnology
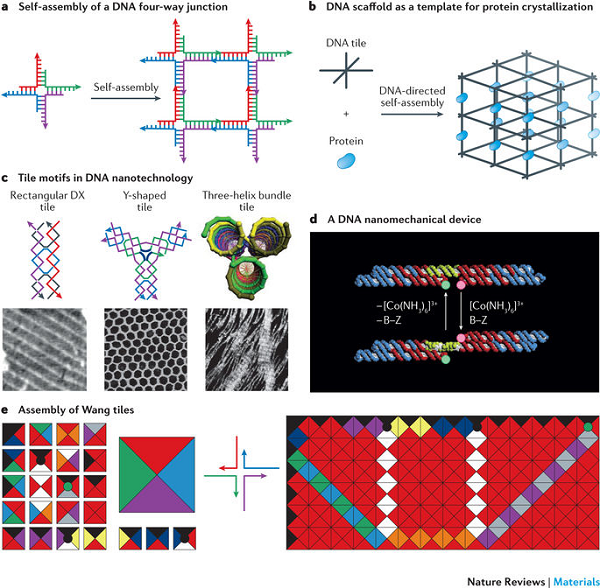
Figure 1 Development of DNA nanotechnology
DNA is a molecule that stores and transmits genetic information in biological systems. The field of DNA nanotechnology takes this molecule out of its biological background and uses its information to assemble the structure and then join them together. Recently, New York University Nadrian C. Seeman and McGill University Hanadi F. Sleiman (Communications) summarized the methods used to assemble DNA nanostructures and described their biophysics, diagnostics, nanoparticle and protein assembly. Emerging applications in biomolecule structure determination, drug delivery and synthetic biology. The application of orthogonal interaction in DNA nanostructures is discussed. Finally, the future development direction of this field is prospected.
2. Chemical Society Reviews: Recent Developments in Two-Dimensional Inorganic Quantum Dots
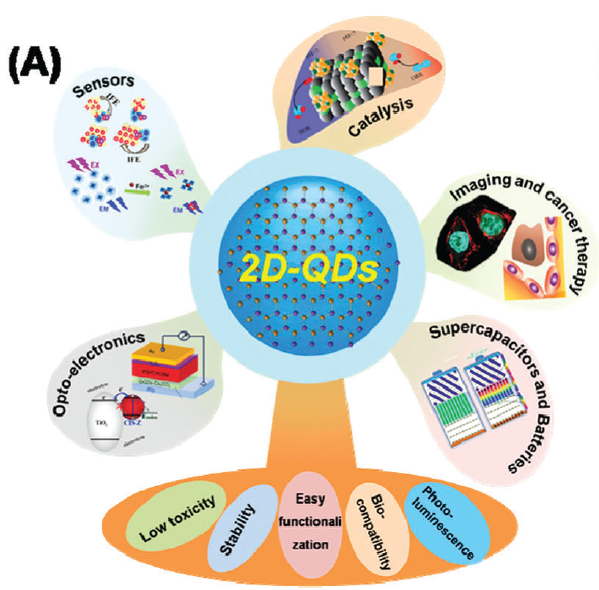
Figure 2 Application of two-dimensional (2D) inorganic-based quantum dots
The development of two-dimensional (2D) inorganic-based quantum dots (QDs) is still in its infancy, but due to its high chemical stability, good water dispersibility, excellent optical properties, good biocompatibility and easy functionalization, Has caused great concern to researchers. Recently, the review by Guo Shaojun of Peking University and Xu Yuanhong (Common Communications) of Qingdao University covers almost all graphene, phospholene, silene, carbide, nitride, transition metal dichalcogenide, transition metal. 2D-QDs of oxides and MXenes. Introduced their categories, synthetic routes, performance, functionality and applications. In the application section, advances in bioimaging, cancer therapy, fluorescence sensing and optoelectronics are highlighted.
3. Chemical Society Reviews: Magnetic Functions in MOFs: From Frame to Pore
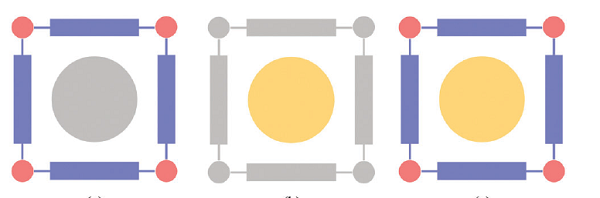
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of magnetic MOFs
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), also known as porous coordination polymers (PCPs), emerged about 30 years ago as revolutionary materials used in various fields of society and industry, such as storage of fuels (hydrogen and methane), and capture of gases ( Such as greenhouse gases), separation, drug delivery and catalysis, etc. The common feature of all these frameworks assembled from inorganic subunits (metal centers, clusters, chains...) and organic linkers (carboxylates, phosphonates, azolates, etc.) is their permanent Porosity. Recently, the University of Valencia Guillermo MÃnguez Espallargas, Eugenio Coronado (Common Communications) and others have demonstrated the different methods developed to date to prepare electronically functional metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), especially in magnetic research. The article introduces the chemical design of the framework necessary for different magnetic phenomena, as well as the encapsulation of functional substances in their pores, and realizes the hybrid multifunctional MOFs with an extended lattice of a molecular lattice.
4. Chemical Society Reviews: Recent advances in the assembly of nanodevices and van der Waals heterostructures
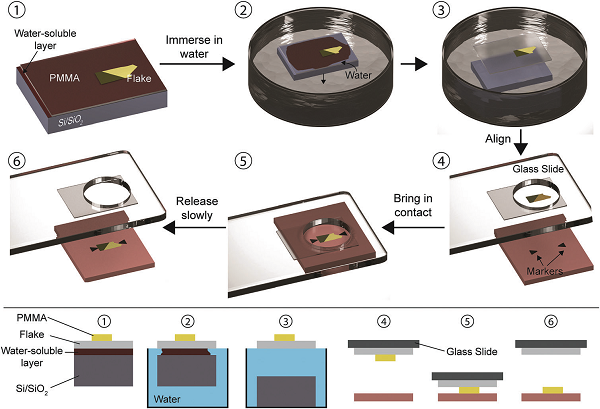
Figure 4 deterministic placement method diagram
Due to the recently developed deterministic placement method for transporting two-dimensional (2D) materials, heterostructures can now achieve high-precision layer-by-layer assembly. In addition, these deterministic placement methods open the door to the fabrication of complex devices that would otherwise be difficult to achieve with traditional bottom-up nanofabrication methods, not to mention the fabrication of fully packaged devices with sophisticated electronic properties. Recently, Riccardo Frisenda of the Institute of Advanced Studies in Nanoscience and Technology in Madrid, Spain and Andres Castellanos-Gomez (Common Communications) of the Institute of Materials Science in Madrid reviewed the current status of deterministic placement methods and described and compared the different alternative methods available in the literature. Describes their potential to manufacture van der Waals heterostructures, integrate 2D materials into complex devices, and fabricate man-made two-layer structures.
5. Chemical Society Reviews: Metal-organic framework membranes for liquid separation
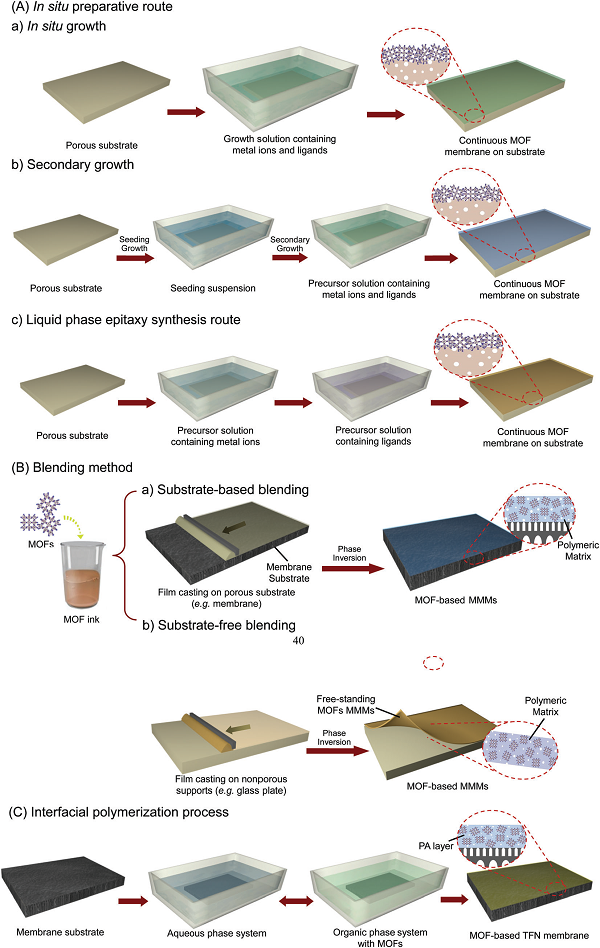
Figure 5 Flow chart of metal organic frame membrane for liquid separation
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) represent a class of fascinating solid crystalline materials that can be self-assembled in a simple manner by coordination of metal ions or clusters with organic ligands. Recently, Li Jiansheng of Nanjing University of Science and Technology and Bart Van der Bruggen (corresponding author) of Leuven University highlighted the application of MOF base film in the field of liquid separation. The criteria for the rational selection of MOFs in the fabrication of MOF-based films are given. The article introduces the rational design strategy of MOF membrane and the latest application progress in the field of liquid separation such as pervaporation, water treatment and organic solvent nanofiltration. In addition, some attractive dual-functions of MOF-based membranes have been discussed for their application in removing micro-contaminants, degradation and antimicrobial activity. Finally, the article clarifies the challenges and future opportunities in this area.
6. Chemical Reviews: Effect of O2 Activity on Metal Surfaces on Heterogeneous Catalyst Binding and Reactivity
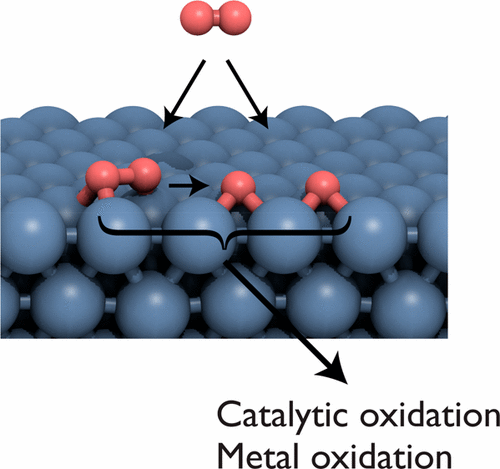
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of the microstructure of the catalytic reaction
The activation of O2 on the metal surface is a key process for heterogeneous catalysis and material oxidation. Recently, Harvard University's Cynthia M. Friend (communication author) team discussed the trend of O2 activation on transition metal surfaces, and described various O2 adsorption states from two aspects of electronic structure and geometry. The mechanism and kinetics of O2 decomposition, including the importance of spin-change, are also discussed. The reactivity of O2 and O to reactant molecules is also briefly discussed in the context of catalysis. The reactivity of the surface to O2 is generally related to the adsorption strength of O, the tendency to oxidize, and the heat of oxide formation. The periodicity can be adjusted by interaction with the attraction and repulsion of the d-band such that the inert metal tends to have a full d-band of low energy and has a large spatial overlap with the adsorbed state.
7. Overview of the Accounts of Chemical Research: Electrode-electrolyte interface for liquid or inorganic solid electrolytes in lithium-sulfur batteries
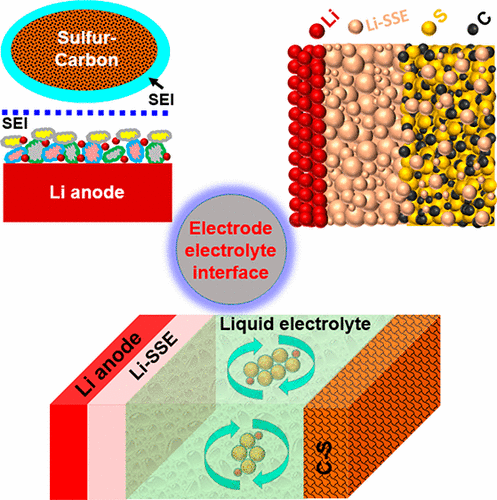
Figure 7 Electrode-electrolyte interface microanalysis
Electrode-electrolyte interface properties play a key role in the cycling performance of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) cells. Recently, the team of Arumugam Manthiram (Corresponding Author) of the University of Texas at Austin first summarized the latest technical contributions of the Solid Electrolyte Interface (SEI) formed on lithium metal anodes and sulfur cathodes in conventional liquid electrolyte Li-S batteries and recent Some strategies proposed to improve the stability of SEI. At the same time, the article describes that solid Li+ conductive electrolytes have been tried to develop Li-S batteries to eliminate polysulfide shuttle problems. The authors clarify that in addition to the low ionic conductivity of solid electrolytes, the key issue is the poor interfacial properties between the electrodes and the solid electrolyte. The article also reviews the progress of the two electrodes and solid electrolyte interface of "all solid lithium-sulfur battery" and "mixed electrolyte lithium-sulfur battery".
Here you can find the related products in Ultrasonic Flow Meter, we are professional manufacturer of Ultrasonic Flow Meter,Portable Flow Meter,Portable Ultrasonic Flow Meter,Ultrasonic Flow Measurement. We focused on international export product development, production and sales. We have improved quality control processes of Ultrasonic Flow Meter to ensure each export qualified product.
If you want to know more about the products in Ultrasonic Flow Meter, please click the product details to view parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Ultrasonic Flow Meter,Portable Flow Meter,Portable Ultrasonic Flow Meter,Ultrasonic Flow Measurement.
Whatever you are a group or individual, we will do our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive message about Ultrasonic Flow Meter!
Ultrasonic Flow Meter,Portable Flow Meter,Portable Ultrasonic Flow Meter,Ultrasonic Flow Measurement
Xi'an Gavin Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.gaimcmeaso.com
