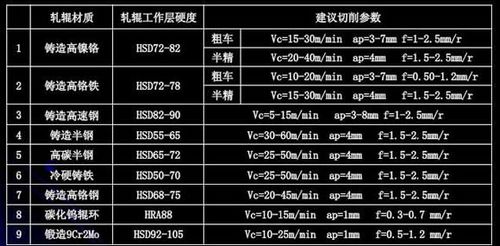
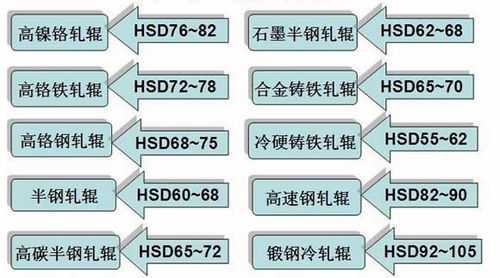
**First, the selection of machine clamp tools commonly used in roll turning:**
Heavy-duty rolls are typically processed using heavy-duty roll lathes, and square inserts such as 40x40 are frequently used. Common shank angles include 45-degree cutting tools and round insert tools. Smaller rolls may also use 25x25 or 32x32 holders. The main cutting edge angle is selected based on the "long diameter ratio" of the roll. For slender rolls, a 90° or 75° tool is usually preferred, while thicker rolls are often machined with 45° or round inserts.
**Second, selecting CBN insert sizes according to cutting parameters and processing conditions:**
When using BN-K1 grade cubic boron nitride (CBN) inserts for cast iron rolls, common size models include RNMN200800, RNUN200800, RNMN150700, RNUN160800, RNUN150716, and RNMN150716.
For forged steel cold rolls, BN-S20 grade CBN inserts are typically used, with common blade types such as SNMN120712, SNMN120412, SNMN120408, and RNMN120400.
The turning tool and CBN insert are shown in the figure below:
4o

Optoelectronic Chips
CHENGDU MESKERNEL INTEGRATED TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.meskernel.com
