Nano Letters, the authoritative journal of nanomaterial science sponsored by the American Chemical Society, recently published the paper "Ferromagnetism in Semihydrogenated graphene sheet" by Professor Sun Qiang, Department of Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology, School of Applied Physics and Technology, Peking University. (http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdfplus/10.1021/nl9020733), reporting their latest work on single-layer graphene magnetics.
Graphene is one of the most hot research fields in the world. It is a non-magnetic metal material with zero band gap, and it has many novel physical properties and broad application prospects. In order to make graphene magnetic, scientists have proposed various methods including cutting it into a zero-dimensional or one-dimensional nano-ribbon structure with a zigzag configuration, or generating defects and introducing impurity atoms. The existing methods not only destroy the structural integrity of graphene, but also produce a non-uniform distribution of magnetic properties, and it is difficult to control experimentally. Professor Sun Qiang's research group first proposed the idea of ​​achieving ferromagnetism in graphene by semi-hydrogenation, and named semi-hydrogenated graphene as graphone, which is a new structural form introduced after graphene, graphane. Professor Sun Qiang's research group applied spin-polarization density functional theory. It was found that when hydrogen atoms are adsorbed on some carbon atoms of graphene, the π bond of graphene is destroyed, resulting in each carbon atom not hydrogenated. An unpaired 2p electron with long-range exchange coupling between them forms a stable ferromagnet with a Curie temperature of approximately 278 ~ 417 K. This is more controllable and operability than the currently known methods. It not only maintains the integrity of the graphene skeleton structure and the uniform distribution of magnetic properties, but also avoids the magnetic properties caused by the assembly of the nano-ribbon. The annihilation. The research results will broaden the application prospects of graphene sheet, which is expected to be used in many fields such as spintronics and microelectronics. Reviewers of Nano Letters spoke highly of the work, pointing out "The manuscript presents nice new scientific ideas and concepts. It certainly will trigger new experiments...", "The ideas are inspiring...".
Zhou Jian, the first author of the paper, is a graduate student of Professor Qian Qiang. The co-authors of the paper include Associate Professor Wang Qian, Professor of Physics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Professor P. Jena, Researcher Chen Xiaoshuang, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Tohoku University. Professor Y. Kawazoe, Institute of Metal Materials. The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
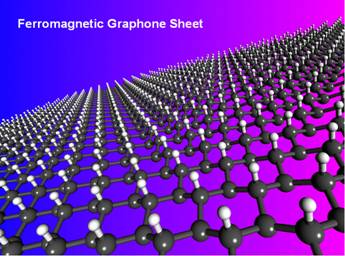
Structural model of ferromagnetic two-dimensional graphone sheet
Dengue IgG/IgM diagnostic test detects two classes of antibodies, immunoglobulin G and M, in serum/plasma or blood by using specific complementary antibody markers. Diagnosis may require multiple tests because the body's immune system produces varying amounts of antibodies as the disease progresses. It takes about 20 minutes for the test to give a result.

Dengue Rapid Test Kits,Accuracy up to 98%,Rapid diagnosis, results in 15 minutes
Yong Yue Medical Technology(Kunshan) Co.,Ltd , https://www.yongyuecultureplate.com
